1. The University which telecasts interaction educational programmes through its own channel is
(A) Osmania University
(B) University of Pune
(C) Annamalai University
(D) Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU)
2. Which of the following skills are needed for present day teacher to adjust effectively with the classroom teaching ?
1. Knowledge of technology
2. Use of technology in teaching learning
3. Knowledge of students’ needs
4. Content mastery
(A) 1 & 3 (B) 2 & 3 (C) 2, 3 & 4 (D) 2 & 4
3. Who has signed an MOU for Accreditation of Teacher Education Institutions in India ?
(A) NAAC and UGC (B) NCTE and NAAC (C) UGC and NCTE (D) NCTE and IGNOU
4. The primary duty of the teacher is to
(A) raise the intellectual standard of the students
(B) improve the physical standard of the students
(C) help all round development of the students
(D) imbibe value system in the students
5. Micro teaching is more effective
(A) during the preparation for teaching-practice
(B) during the teaching-practice
(C) after the teaching-practice
(D) always
6. What quality the students like the most in a teacher ?
(A) Idealist philosophy (B) Compassion (C) Discipline (D) Entertaining
7. A null hypothesis is
(A) when there is no difference between the variables
(B) the same as research hypothesis
(C) subjective in nature
(D) when there is difference between the variables
8. The research which is exploring new facts through the study of the past is called
(A) Philosophical research (B) Historical research (C) Mythological research (D) Content analysis
9. Action research is
(A) An applied research
(B) A research carried out to solve immediate problems
(C) A longitudinal research
(D) Simulative research
10. The process not needed in Experimental Researches is
(A) Observation (B) Manipulation (C) Controlling (D) Content Analysis
11. Manipulation is always a part of
(A) Historical research (B) Fundamental research (C) Descriptive research (D) Experimental research
12. Which correlation co-efficient best explains the relationship between creativity and intelligence ?
(A) 1.00 (B) 0.6 (C) 0.5 (D) 0.3
Read the following passage and answer the Question Nos. 13 to 18 :
The decisive shift in British Policy really came about under mass pressure in the autumn and winter of 1945 to 46 – the months which Perderel Moon while editing Wavell’s Journal has perceptively described as ‘The Edge of a Volcano’. Very foolishly, the British initially decided to hold public trials of several hundreds of the
20,000 I.N.A. prisoners (as well as dismissing from service and detaining without trial no less than 7,000). They compounded the folly by holding the first trial in the Red Fort, Delhi in November 1945, and putting on the dock together a Hindu, a Muslim and a Sikh (P.K. Sehgal, Shah Nawaz, Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon). Bhulabhai Desai, Tejbahadur Sapru and Nehru appeared for the defence (the latter putting on his barrister’s gown after 25 years), and the Muslim League also joined the countrywide protest. On 20 November, an Intelligence Bureau note admitted that “there has seldom been a matter which has attracted so much Indian public interest and, it is safe to say, sympathy … this particular brand of sympathy cuts across communal barriers.’ A journalist (B. Shiva Rao) visiting the Red Fort prisoners on the same day reported that
‘There is not the slightest feeling among them of Hindu and Muslim … A majority of the men now awaiting trial in the Red Fort is Muslim. Some of these men are bitter that Mr. Jinnah is keeping alive a controversy about Pakistan.’ The British became extremely nervous about the I.N.A. spirit spreading to the Indian Army, and in January the Punjab Governor reported that a Lahore reception for released I.N.A. prisoners had
been attended by Indian soldiers in uniform.
13. Which heading is more appropriate to assign to the above passage ?
(A) Wavell’s Journal (B) Role of Muslim League (C) I.N.A. Trials (D) Red Fort Prisoners
14. The trial of P.K. Sehgal, Shah Nawaz and Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon symbolises
(A) communal harmony
(B) threat to all religious persons
(C) threat to persons fighting for the freedom
(D) British reaction against the natives
15. I.N.A. stands for
(A) Indian National Assembly (B) Indian National Association
(C) Inter-national Association (D) Indian National Army
16. ‘There has seldom been a matter which has attracted so much Indian Public Interest and, it is safe to say, sympathy … this particular brand of sympathy cuts across communal barriers.’
Who sympathises to whom and against whom ?
(A) Muslims sympathised with Shah Nawaz against the British
(B) Hindus sympathised with P.K. Sehgal against the British
(C) Sikhs sympathised with Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon against the British
(D) Indians sympathised with the persons who were to be trialled
17. The majority of people waiting for trial outside the Red Fort and criticising Jinnah were the
(A) Hindus (B) Muslims (C) Sikhs (D) Hindus and Muslims both
18. The sympathy of Indian soldiers in uniform with the released I.N.A. prisoners at Lahore indicates
(A) Feeling of Nationalism and Fraternity
(B) Rebellious nature of Indian soldiers
(C) Simply to participate in the reception party
(D) None of the above
19. The country which has the distinction of having the two largest circulated newspapers in the world is
(A) Great Britain (B) The United States (C) Japan (D) China
20. The chronological order of non-verbal communication is
(A) Signs, symbols, codes, colours
(B) Symbols, codes, signs, colours
(C) Colours, signs, codes, symbols
(D) Codes, colours, symbols, signs
21. Which of the following statements is not connected with communication ?
(A) Medium is the message.
(B) The world is an electronic cocoon.
(C) Information is power.
(D) Telepathy is technological.
22. Communication becomes circular when
(A) the decoder becomes an encoder
(B) the feedback is absent
(C) the source is credible
(D) the channel is clear
23. The site that played a major role during the terrorist attack on Mumbai (26/11) in 2008 was
(A) Orkut (B) Facebook (C) Amazon.com (D) Twitter
24. Assertion (A) : For an effective classroom communication at times it is desirable to use the projection technology.
Reason (R) : Using the projection technology facilitates extensive coverage of course contents.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation.
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation.
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
25. January 1, 1995 was a Sunday. What day of the week lies on January 1, 1996 ?
(A) Sunday (B) Monday (C) Wednesday (D) Saturday
26. When an error of 1% is made in the length and breadth of a rectangle, the percentage error (%) in the area of a rectangle will be
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 4
27. The next number in the series 2, 5, 9, 19, 37, ? will be
(A) 74 (B) 75 (C) 76 (D) None of the above
28. There are 10 true-false questions in an examination. Then these questions can be answered in
(A) 20 ways (B) 100 ways (C) 240 ways (D) 1024 ways
29. What will be the next term in the following ? DCXW, FEVU, HGTS, ?
(A) AKPO (B) ABYZ (C) JIRQ (D) LMRS
30. Three individuals X, Y, Z hired a car on a sharing basis and paid Rs. 1,040. They used it for 7, 8, 11 hours, respectively. What are the charges paid by Y ?
(A) Rs. 290 (B) Rs. 320 (C) Rs. 360 (D) Rs. 440
31. Deductive argument involves
(A) sufficient evidence (B) critical thinking (C) seeing logical relations (D) repeated observation
32. Inductive reasoning is based on or presupposes
(A) uniformity of nature (B) God created the world (C) unity of nature (D) laws of nature
33. To be critical, thinking must be
(A) practical (B) socially relevant (C) individually satisfying (D) analytical
34. Which of the following is an analogous statement ?
(A) Man is like God
(B) God is great
(C) Gandhiji is the Father of the Nation
(D) Man is a rational being.
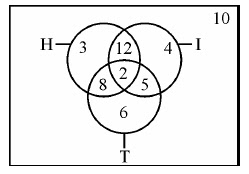
Questions from 35 - 36 are based on the following diagram in which there are three intersecting circles.
H representing The Hindu, I representing Indian Express and T representing The Times of India. A total of 50 persons were surveyed and the number in the Venn diagram indicates the number of persons reading the newspapers.
35. How many persons would be reading at least two newspapers ?
(A) 23 (B) 25 (C) 27 (D) 29
36. How many persons would be reading almost two newspapers ?
(A) 23 (B) 25 (C) 27 (D) 48
37. Which of the following graphs does not represent regular (periodic) behaviour of the variable f(t) ?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
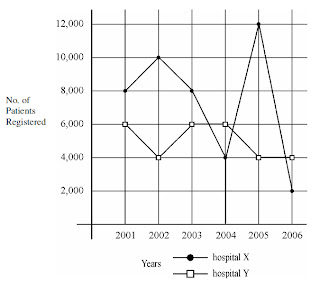
Study the following graph and answer the questions 38 to 40 :
38. In which year total number of patients registered in hospital X and hospital Y was the maximum ?
(A) 2003 (B) 2004 (C) 2005 (D) 2006
39. What is the maximum dispersion in the registration of patients in the two hospitals in a year ?
(A) 8000 (B) 6000 (C) 4000 (D) 2000
40. In which year there was maximum decrease in registration of patients in hospital X ?
(A) 2003 (B) 2004 (C) 2005 (D) 2006
[For Blind Students Only]
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions 35 to 40 :
London’s phenomenal growth was probably at its fastest in the sixteenth century, a period when the population was growing everywhere. Many people were attracted to the rapidly growing port, which handled upto 90% of total English foreign trade and gave rise to a wide range of ancillary industries. Other sectors provided goods and services for the court, which now settled permanently in the capital, and for the growing numbers of the rich and ambitious who were attracted by court’s presence. This concentration of the wealthy made London a great leisure centre and the main purveyor of professional services, especially in medicine and law. Population growth now tended to become cumulative. More people needed even more people to provide them with goods and services that they required to survive in a large city. London was always an unhealthy place and mortality rates were much higher than elsewhere in the country, sometime rising to catastrophic heights, as in the terrible plagues of 1603, 1625 and 1665, the last of which killed 80,000 people, 1/6th of the total population of the city. Such high death rates coupled with rather low fertility, meant that London could never grow by its own natural increase. In the century after 1650, when London continued to grow but the English population remained fairly stable, immigration to the city drained the countryside of people and gave London its highest-yet population. It has probably then, in the early eighteenth century London of Defoe and Hogarth, that the city also had its greatest significance as a school centre and a school of manners and ideas for the rest of the country.
35. London’s rate of population increase was at its greatest in the seventeenth century because
(A) Its death rate was the highest in Britain at that time
(B) It was a time when the population growth was declining everywhere
(C) Migrants were drawn to London because of the vast increase in trading
(D) Its high rate of mortality was offset by a low birthrate
36. In comparison to the rest of the country, the population decline in London in the seventeenth century was as a result of
(A) frequent outbreaks of plague
(B) low rate of fertility
(C) immigration to other parts of the country
(D) movement of people to other countries
37. After 1600 A.D., the demography of London was characterised by
(A) high deathrates and birthrates
(B) three major outbreaks of disease, the last of which was responsible for the death of over 80,000 people
(C) a rise in population through natural growth
(D) population stability
38. Examples of the economic hegemony of London in the seventeenth century include
(A) the movement of the Court permanently to the capital
(B) 9/10th of England’s overseas trade passing through its docks
(C) a large variety of secondary industries growing up around the port of London.
(D) London becoming England’s major intellectual and cultural centre at the time of Defoe and Hogarth.
39. Which one of the following was not the cause of high rate of death among the people of London ?
(A) Increasing low fertility among people
(B) Absence of diseases
(C) Family planning regulations of the State
(D) Migration of population
40. What made London a great leisure centre ?
(A) Growth of ancillary industries.
(B) Concentration of wealth among people who were earlier poor.
(C) Increased rate of mortality.
(D) Due to increase in immigrant population.
41. Which of the following sources of data is not based on primary data collection ?
(A) Census of India (B) National Sample Survey
(C) Statistical Abstracts of India (D) National Family Health Survey
42. Which of the four data sets have more dispersion ?
(A) 88 91 90 92 89 91
(B) 0 1 1 0 –1 –2
(C) 3 5 2 4 1 5
(D) 0 5 8 10 –2 –8
43. Which of the following is not related to information security on the Internet ?
(A) Data Encryption (B) Water marking (C) Data Hiding (D) Information Retrieval
44. Which is the largest unit of storage among the following ?
(A) Terabyte (B) Megabyte (C) Kilobyte (D) Gigabyte
45. bit stands for
(A) binary information term (B) binary digit (C) binary tree (D) Bivariate Theory
46. Which one of the following is not a linear data structure ?
(A) Array (B) Binary Tree (C) Queue (D) Stack
47. Which one of the following is not a network device ?
(A) Router (B) Switch (C) Hub (D) CPU
48. A compiler is used to convert the following to object code which can be executed
(A) High-level language (B) Low-level language (C) Assembly language (D) Natural language
49. The great Indian Bustard bird is found in
(A) Thar Desert of Rajasthan (B) Coastal regions of India (C) Malabar Coast (D) Delta regions
50. The Sagarmanthan National Park has been established to preserve the eco-system of which mountain peak ?
(A) Kanchenjunga (B) Mount Everest (C) Annapurna (D) Dhaulavira
51. Maximum soot is released from
(A) Petrol vehicles (B) CNG vehicles (C) Diesel vehicles (D) Thermal Power Plants
52. Surface Ozone is produced from
(A) Transport sector (B) Cement plants (C) Textile industry (D) Chemical industry
53. Which one of the following non-conventional energy sources can be exploited most economically ?
(A) Solar
(B) Wind
(C) Geo-thermal
(D) Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)
54. The most recurring natural hazard in India is
(A) Earthquakes (B) Floods (C) Landslides (D) Volcanoes
55. The recommendation of National Knowledge Commission for the establishment of
1500 Universities is to
(A) create more teaching jobs
(B) ensure increase in student enrolment in higher education
(C) replace or substitute the privately managed higher education institutions by public institutions
(D) enable increased movement of students from rural areas to urban areas
56. According to Article 120 of the Constitution of India, the business in Parliament shall
be transacted in
(A) English only
(B) Hindi only
(C) English and Hindi both
(D) All the languages included in Eighth Schedule of the Constitution
57. Which of the following is more interactive and student centric ?
(A) Seminar (B) Workshop (C) Lecture (D) Group Discussion
58. The Parliament in India is composed of
(A) Lok Sabha & Rajya Sabha
(B) Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha & Vice President
(C) Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha & President
(D) Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha with their Secretariats
59. The enrolment in higher education in India is contributed both by Formal System of Education and by System of Distance Education. Distance education contributes
(A) 50% of formal system
(B) 25% of formal system
(C) 10% of the formal system
(D) Distance education system’s contribution is not taken into account while considering the figures of enrolment in higher education
60. Assertion (A) : The U.G.C. Academic Staff Colleges came into existence to improve the quality of teachers.
Reason (R) : University and college teachers have to undergo both orientation and refresher courses.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation.
(B) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is correct and (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false and (R) is correct.

No comments:
Post a Comment